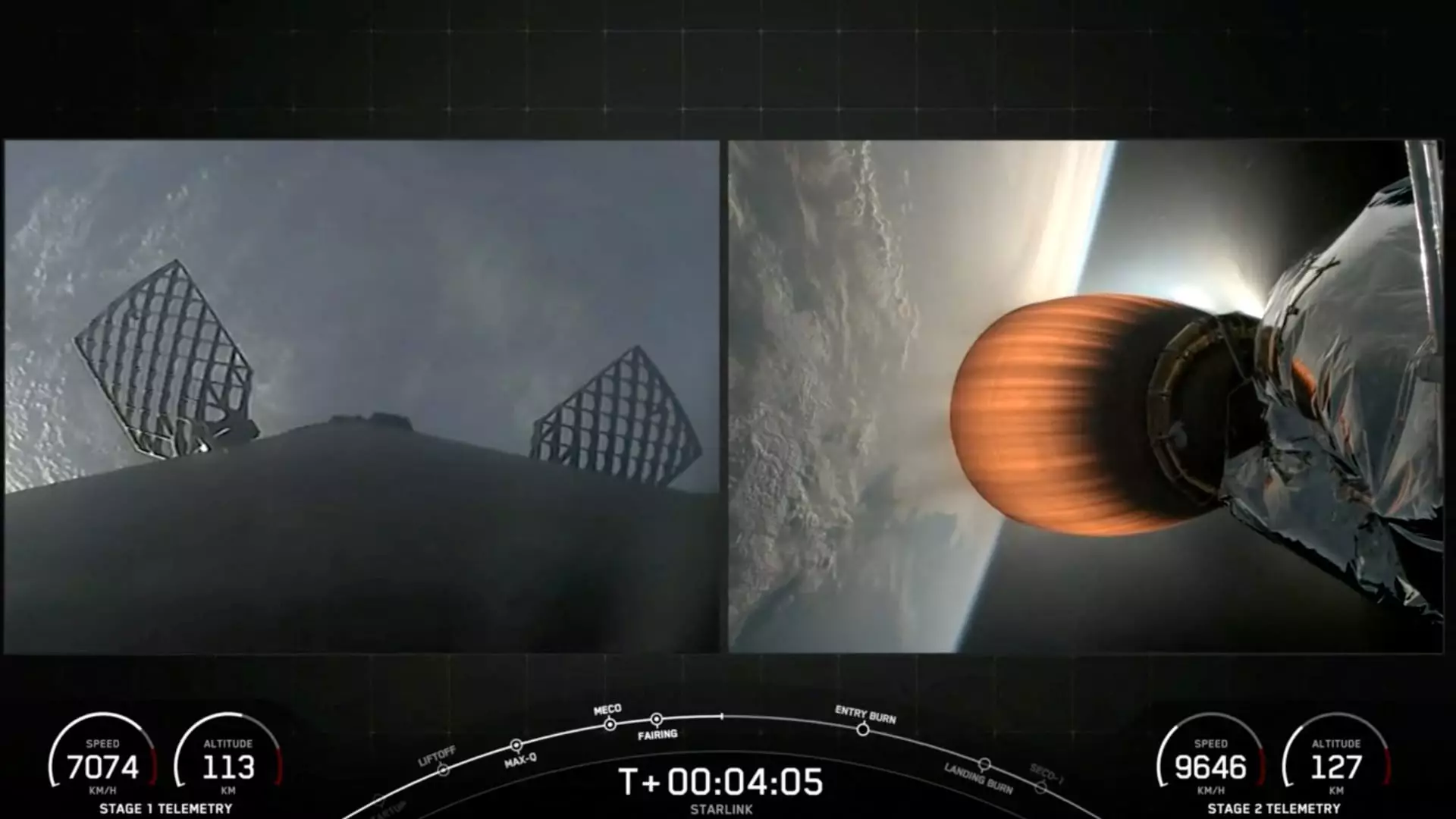
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket faced an unexpected setback recently when an inflight failure occurred, resulting in the grounding of the vehicle. The incident took place during the “Starlink Group 9-3” mission, which was launched from California’s Vandenberg Space Force Base with the goal of deploying 20 satellites into low Earth orbit. While the lower first stage of the rocket performed as expected, the upper second stage encountered difficulties when attempting to reignite its engine. This failure ultimately led to the destruction of the second stage, prompting SpaceX CEO Elon Musk to disclose that the engine shutdown was due to reasons that are currently unknown.
Following the incident, SpaceX initiated an investigation into the engine failure, with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) overseeing the process. The FAA confirmed that Falcon 9 will remain grounded until SpaceX’s investigation is completed and the agency approves the final report, including any necessary corrective actions. As a result of the investigation, the scheduled launches for the upcoming weeks, including the private Polaris Dawn mission and NASA’s Crew-9, are expected to suffer delays.
Despite the failure of the second stage engine, SpaceX managed to deploy 20 Starlink satellites into orbit. However, due to the lower-than-intended orbit caused by the engine malfunction, the company announced that the satellites will not be recoverable. SpaceX attempted to salvage the situation by making contact with 10 of the satellites to utilize their onboard thrusters to adjust their orbit. Unfortunately, the high-drag environment in the incorrect orbit proved to be too challenging, leading to the decision that the satellites will re-enter Earth’s atmosphere and burn up. SpaceX assured that this situation poses no threat to other satellites in orbit or public safety.
Until this recent incident, Falcon 9 had enjoyed an impressive track record of success, with over 300 consecutive orbital launches completed without issues. The rocket’s last inflight failure occurred in June 2015 during the NASA cargo mission CRS-7. Overall, Falcon 9 has undertaken 354 missions to orbit, showcasing a remarkable achievement of successful landings and rocket booster reuse on more than 280 occasions.
The unexpected engine failure of Falcon 9 serves as a reminder of the inherent risks associated with space exploration and rocket launches. SpaceX’s commitment to safety and thorough investigation processes will be crucial in understanding the root cause of the incident and implementing measures to prevent similar occurrences in the future. Despite this setback, the company’s track record of innovation and resilience suggests that SpaceX will overcome this challenge and continue to push the boundaries of space technology.